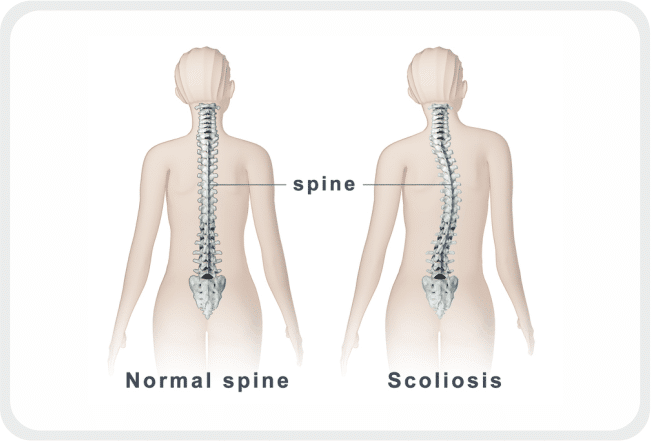
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is defined as a deviation of the normal vertical line of spine, consisting of a lateral curvature with rotation of the vertebrae within the curve. There should be at least 10 degrees of spinal angulation on posterior anterior radiograph with vertebral body rotation. This usually involves thoracic and lumbar regions.
Classification:
- Structural scoliosis: irreversible lateral curvature with fixed rotation of the vertebrae. Rotation of the vertebrae is towards the convexity of the curve. A rib hump is detected on forward bending.
- Nonstructural scoliosis is reversible and can be changed with forwarding or side bending or with the realignment of the pelvis by correction of a leg-length discrepancy. It is also called functional or postural scoliosis.
Causes:
- Structural scoliosis: due to neuromuscular disorders, osteopathic disorders (osteomalacia, rickets, fracture) and idiopathic disorders where the cause is unknown.
- Nonstructural scoliosis: due to leg-length discrepancy, muscle guarding or spasm from a painful stimulus in the back or neck or habitual postures.
Muscle impairments and Symptoms:
- Mobility impairment on the concave side of the curve.
- Impaired muscle function due to stretch and weakening on the convex side.
- With advanced structural scoliosis, cardiopulmonary functions restrict.
- Nerve root irritation on the side of concavity.
- Pain from mechanical stresses to sensitive structures and from muscle tension.
Treatment:
- Develop awareness and control of spinal alignment in a variety of positions.
- Educate the relationship of symptoms with sustained or repetitive postures.
- Increased mobility in restricting muscles, joints, fascia by manual or self-stretching and joint mobilization.
- Learn safe body mechanics with functional exercises.
- Learn to correct stress-provoking postures/activities by developing a recreational environment.
- Learn stress management/ relaxation by breathing exercises.
- Improve aerobic capacity.
- Development of neuromuscular control, strength, and endurance in postural and extremity muscles.







