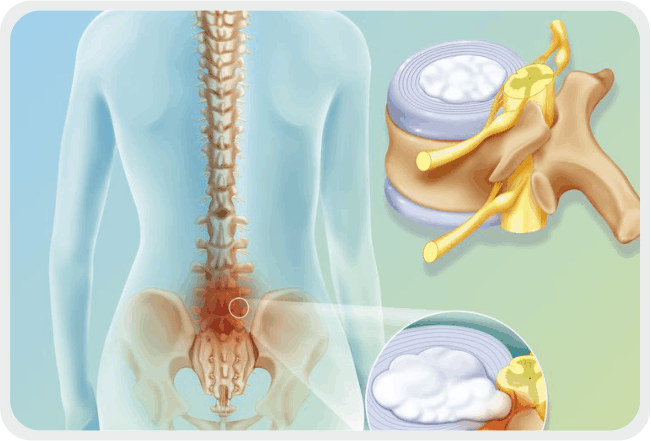
Disc Prolapse
Disc prolapse is a rupture of the nuclear material into the vertebral canal caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. The discs are quite flexible and impart flexibility to the motion of the spinal cord. A disc consists of a soft material called nucleus pulposus enclosed in a strong layer of outer fibers called annulus fibrosus.
Risk Factors:
- You could be at risk if you:
- Lift heavy weights frequently.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Having anatomical abnormalities.
- Degenerative disorders
- Participate in high-impact sports.
Signs and symptoms:
- Pain –arises from the pressure of disc against pain-sensitive structures such as ligaments, nerve roots, dura mater.
- Neurological signs- myotomal weakness and dermatomal sensory changes.
- Loss of bladder control and saddle anaesthesia.
- Back pain
- Neck pain
- Posture may shift to one side called list.
- Forward bending, coughing increases the pain in the back or neck.
Treatment:
- Educate the patient about precautions and the condition such as obesity, postural changes to reduce stress on the spine.
- Decrease the symptoms by mobilizations, soft tissue manipulation, relaxation techniques.
- Teach awareness of neck and pelvic position and movements by kinesthetic training.
- Initiate neuromuscular activation and control of stabilizing muscles.
- Avoiding hazardous activities that may aggravate the symptoms.
Prevention:
- Use proper lifting techniques.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Exercise regularly to keep muscles strong.
- Stop smoking.
- Eat a healthy and well-balanced meal.
- Do not wear high heeled shoes to avoid back problems.
Management at AktivHealth:
Our Doctor will conduct a thorough examination and may suggest investigation as needed. Depending upon the clinical situation an appropriate disc prolapse treatment plan will be suggested which may be conservative and or surgical intervention.
Because a herniated disk desiccates and shrinks over time, symptoms tend to abate regardless of treatment. Up to 85% of patients with disc pain, regardless of cause, generally show recovery without surgery.
An appropriate program of physical therapy and home exercises will help in improving posture and strengthening back muscles and thus permitting safer spinal movements so as not to further irritate or compress the nerve root.











